Let’s explore each entry in more detail using Printing Plus’s information from Analyzing and Recording Transactions and The Adjustment Process as our example. The Printing Plus adjusted trial balance for January 31, 2019, is presented in Figure 5.4. It is the end of the year, December 31, 2018, and you are reviewing your financials for the entire year. closing entries You see that you earned $120,000 this year in revenue and had expenses for rent, electricity, cable, internet, gas, and food that totaled $70,000. However, if the company also wanted to keep year-to-date information from month to month, a separate set of records could be kept as the company progresses through the remaining months in the year.

However, you might wonder, “Where are the revenue, expense, and dividend accounts? If we expand the view, we’ll find the usual suspects—the temporary accounts. These accounts were reset to zero at the end of the previous year to start afresh. Only income statement accounts help us summarize income, so only income statement accounts should go into income summary. Once all of the required entries have been made, you can run your post-closing trial balance, as well as other reports such as an income statement or statement of retained earnings.
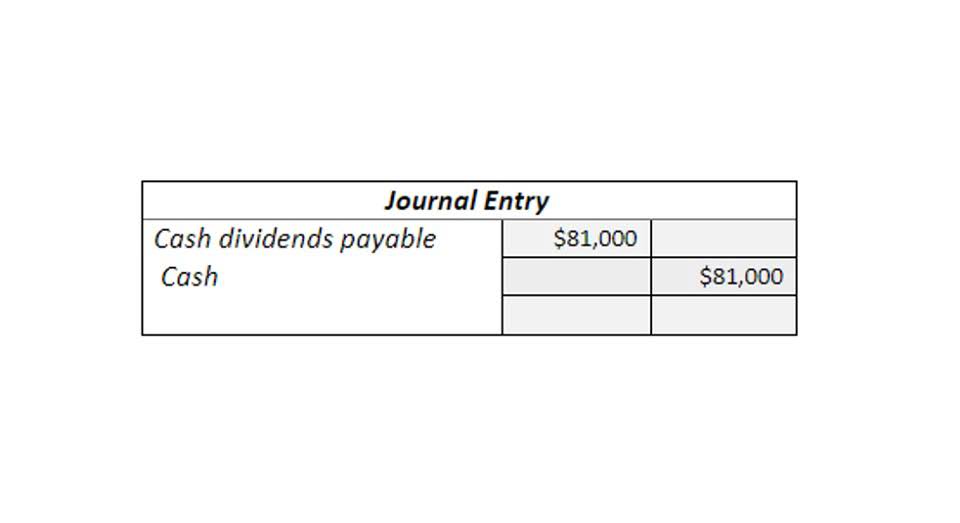
Step 4: Close withdrawals to the capital account
We’ll use a company called MacroAuto that creates and installs specialized exhaust systems for race cars. Here are MacroAuto’s accounting records simplified, using positive numbers for increases and negative numbers for decreases instead of debits and credits in order to save room and to get a higher-level view. The Income Summary balance is ultimately closed to the capital account. The year-end closing is the process of closing the books for the year. This involved reviewing, reconciling, and making sure that all of the details in the ledger add up.
If the Post-Closing Trial Balance is not balanced and the Pre-Closing Trial Balance is balanced, then there were errors in the Closing Entry Process. The following would be an example of a trial balance; you can see that there are no temporary accounts and that all accounts have a natural number balance. The Third Step of Closing Entries is closing the Income Summary Account. Now, if you realize from steps 1 & 2, the balance of the Income Summary is also the same amount as the Net Income. As stated before, Income Summary is a temporary account and would also be closed. Companies are required to close their books at the end of each fiscal year so that they can prepare their annual financial statements and tax returns.
Four Steps in Preparing Closing Entries
To get a zero balance in an expense account, the entry will show a credit to expenses and a debit to Income Summary. Printing Plus has $100 of supplies expense, $75 of depreciation expense–equipment, $5,100 of salaries expense, and $300 of utility expense, each with a debit balance on the adjusted trial balance. The closing entry will credit Supplies Expense, Depreciation Expense–Equipment, Salaries Expense, and Utility Expense, and debit Income Summary.
- It is permanent because it is not closed at the end of each accounting period.
- The purpose of the income summary is to show the net income (revenue less expenses) of the business in more detail before it becomes part of the retained earnings account balance.
- Printing Plus has a $4,665 credit balance in its Income Summary account before closing, so it will debit Income Summary and credit Retained Earnings.
- Printing Plus has $100 of supplies expense, $75 of depreciation expense–equipment, $5,100 of salaries expense, and $300 of utility expense, each with a debit balance on the adjusted trial balance.
